What are the causes of chronic venous disease?
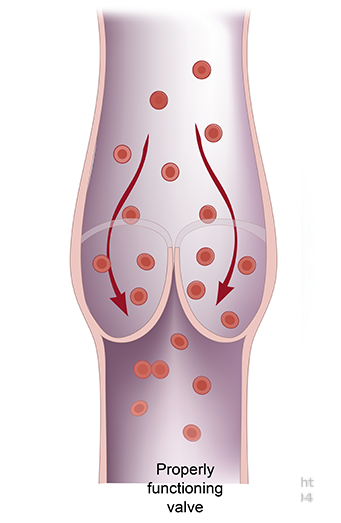
Normally the veins return the blood from the legs with the assistance of a series of one way valves which help to propel the blood out of the legs against gravity. The veins are very thin walled and unlike the arteries they cannot contract to push the blood forward. When patients develop chronic vein disease the valves do not close properly and too much blood pools in the lower extremities. The failure of the valves to close may be hereditary or from scarring due to prior episodes of thrombosis. Other risk factors include, obesity, and prolonged standing or sitting.
What are the symptoms of chronic vein disease?
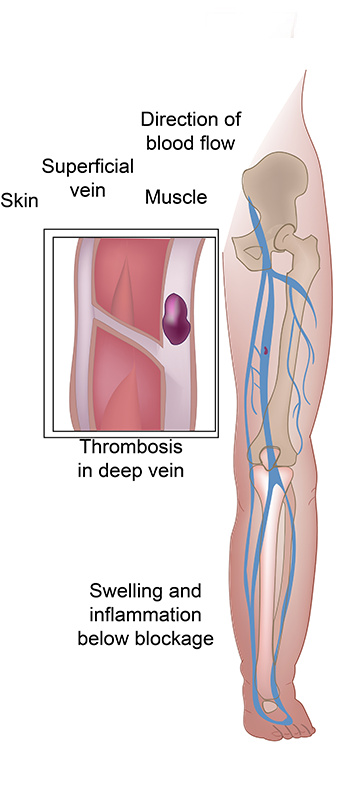
Patients may experience dilation of the veins in the legs which may be painful or cause bleeding. Patients may also have leg swelling, heaviness, fatigue, burning or aching that are worse at the end of the day. As the disease progresses dry and flaky skin may occur in the lower legs causing itching. Later discoloration with ulceration can also develop around the ankles. These wounds can be quite difficult to heal.
How is chronic vein disease diagnosed?
Venous ultrasound with reflux exam is the primary examination done to evaluate all of the veins in the legs. Unlike the regular vein exam which checks only for blood clots, this exam checks for blood clots and evaluates the function of the valves of all the veins of the legs. If you have had a previous ultrasound that checked only for blood clots, your surgeon will need to have another ultrasound preformed to properly evaluate the valve function. Usually the venous ultrasound is the only examination required. Rarely, if a patient has severe swelling that is not explained by the ultrasound exam, a CT scan or a venous angiogram is needed to evaluate the pelvic veins.
What are the treatment options for chronic vein disease?
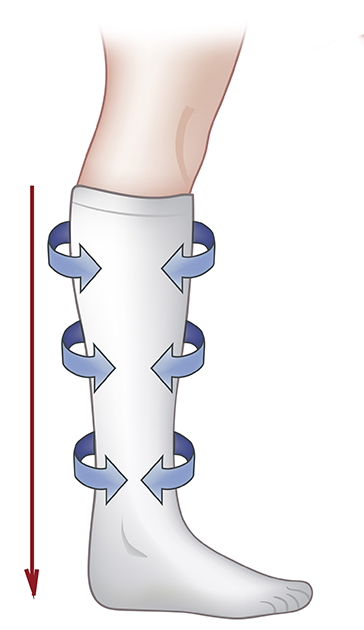
Since the main problem is pooling of blood, as a result of malfunctioning venous valves, conservative treatment is aimed at preventing the blood from pooling in the lower extremities. Compression stockings, leg elevation, regular exercise and weight loss are all very helpful. The compression stockings should be worn during the day and removed in the evening.
If the venous ultrasound shows a valve problem in the superficial veins, and the symptoms are not relieved by compression stockings, your surgeon may suggest a venous ablation procedure. This procedure closes the superficial vein that contain the malfunctioning valves. The blood will be redirected to the deeper veins that in most cases have functional valves. If the deeper veins have better valve function this procedure will improve the symptoms greatly, by increasing the efficiency of blood return from the legs to the heart.
The ablation is done through a small catheter which can be inserted into the vein with ultrasound guidance under local anesthetic. The ablation can be done in the office and the patient can walk immediately afterward with rapid return to normal activities. If the patient has residual large varicose veins, they can be removed also in the office through very small incisions under local anesthesia. If the remaining veins are small, your surgeon may recommend sclerotherapy injections with a very small needles to cause the spider veins to shrink.